- Home Page
- Company Profile
-
Our Products
- Coral Collection Volga
- Continental Collection Riva
- Pearl Collection Volga
- Moon Collection Volga
- Allied Collection Volga
- Onyx Collection Riva
- Lotus Collection Riva
- Rose Collection Riva
- Prince Collection Volga
- Fusion Collection Volga
- Desire Collection Riva
- Opal Collection Volga
- Sapphire Collection Volga
- Flora Collection Riva
- Sensors Collection Volga
- Royal Collection Volga
- Sumo Collection Volga
- Flora Collection Bathroom Accessories
- Versa Collection Volga
- Bathroom Fittings & Accessories
- Cubix Collection Riva
- Squaro Collection Volga
- Choras Collection Volga
- Taj Collection Volga
- Arya Collection Volga
- Blog

What is DERCHI and How Does It Work?
In the rapidly evolving tech landscape, DERCHI stands out as a pivotal concept. DERCHI, a term coined from decentralized energy resources, represents a shift in how we manage energy. According to Dr. Emily Tran, a renowned expert in renewable energy systems, “DERCHI revolutionizes the way we connect energy producers and consumers.”
This innovative framework allows for increased accessibility and efficiency in energy distribution. By integrating various energy sources, DERCHI facilitates a more sustainable energy ecosystem. It encourages collaboration among users, empowering them to contribute to energy generation. However, implementing DERCHI is not without challenges. The technology requires robust infrastructure and regulatory frameworks that can adapt to changing conditions.
Many are excited about the potential of DERCHI, yet reflections on its limitations are critical. Adoption may be inconsistent, as not all regions possess the technological readiness for such integration. Critics voice concerns about equity in access and the potential for unintended consequences. Although DERCHI offers promising developments, careful planning and dialogue are essential for its successful implementation.
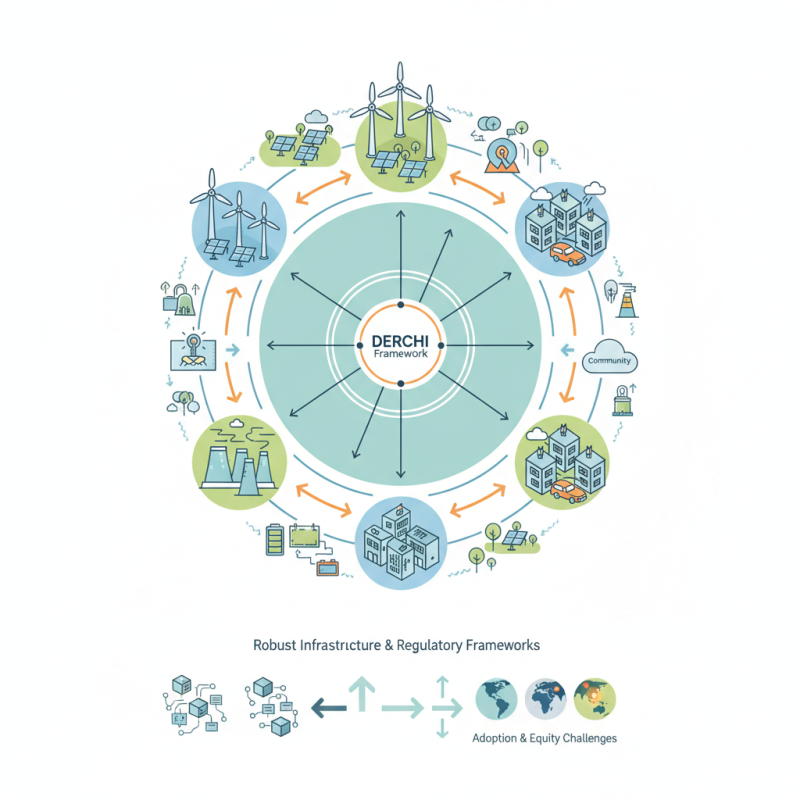
What is DERCHI? An Overview of Decentralized Energy Resource Control Hub
Decentralized Energy Resource Control Hub (DERCHI) represents a significant shift in energy management. This platform empowers users to control their energy resources more effectively. In 2021, the global market for decentralized energy resources was projected to grow at a CAGR of 12.3%, illustrating its increasing relevance.
DERCHI utilizes smart technology to optimize energy use. Households and businesses can integrate solar panels, batteries, and electric vehicles. This integration reduces reliance on traditional grids. According to a report from the International Energy Agency, decentralized solutions could supply 30% of global power by 2030. However, achieving this goal requires robust infrastructure and regulatory support.
One challenge with DERCHI is ensuring interoperability among various technologies. Different devices often use distinct communication protocols, complicating integration. Additionally, user awareness and education are critical. Many consumers may be hesitant to adopt new technologies. Without comprehensive understanding, the potential of DERCHI remains underutilized.
Key Features and Components of DERCHI in Energy Management Systems
DERCHI stands for Distributed Energy Resource Control and Holistic Integration. It plays a vital role in modern energy management systems. DERCHI allows various energy resources to work together. This can include solar panels, wind turbines, and battery storage systems. By coordinating these elements, energy availability becomes more reliable.
Key features of DERCHI include real-time monitoring and analytics. It provides data on energy production and consumption. This data helps in making informed decisions. The system can optimize energy flows. For example, it can store excess energy generated during sunny days. It also addresses the challenges of energy demand peaks.
Another important component is the user interface. An intuitive dashboard can simplify network monitoring. Users need clarity, but not all systems provide it. Many platforms lead to confusion instead of transparency. Moreover, security measures need constant updates. The evolving cyber threats require ongoing vigilance. Overall, DERCHI shows promise, but there's room for improvement.
How DERCHI Facilitates Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
DERCHI is a crucial tool for integrating renewable energy. It provides a platform to manage and optimize energy use. As the use of solar and wind energy grows, the challenges also increase. The intermittent nature of these sources requires effective solutions. According to recent industry reports, renewable energy could account for up to 50% of total energy production by 2030. That means better integration methods are essential.
DERCHI helps address these challenges by facilitating real-time data exchange. Operators can monitor energy flows more effectively. This approach allows for instant adjustments. Reports indicate that smarter integration could reduce energy waste by as much as 30%. However, there are hurdles. Not all regions have the necessary infrastructure. The transition requires investment and thoughtful planning. Data shows that without such efforts, progress could stall.
Moreover, user engagement is vital. The success of DERCHI depends on how well users adapt. Many consumers still struggle with understanding complex systems. The research highlights that enhancing public knowledge could improve adoption rates significantly. Yet, this remains a work in progress. Integrating new technologies demands patience and continued effort from all stakeholders involved.
The Role of DERCHI in Enhancing Grid Reliability and Flexibility
DERCHI, or Distributed Energy Resource Coordination and Hosting Interface, plays a crucial role in enhancing grid reliability and flexibility. By integrating various energy sources, DERCHI facilitates smoother interactions between renewable energies and the traditional grid. This integration allows for better management of energy supply and demand, especially during peak times.
One major benefit of DERCHI is its ability to respond dynamically to changes. For instance, if solar power generation dips due to clouds, DERCHI can quickly adjust to compensate. This flexibility ensures that energy supply remains stable. However, it can be challenging to achieve seamless integration among different energy types. Coordinating these resources requires robust communication and real-time data sharing.
**Tip:** Regularly update your understanding of grid technologies. Staying informed helps users make better decisions regarding energy use.
Another focus of DERCHI is enhancing grid resilience. By decentralizing energy generation, the grid can better withstand disruptions. If one area suffers an outage, other regions can still operate normally. However, this approach demands careful planning and infrastructure investment. Communities must consider their specific needs and energy profiles.
**Tip:** Participate in local energy discussions. Engaging with community initiatives may provide insight into improving local grid systems.
DERCHI Impact on Grid Reliability and Flexibility
This chart illustrates the impact of DERCHI on key performance metrics relevant to grid reliability and flexibility. The values represent a comparative analysis of reliability, flexibility, cost efficiency, and renewable integration, demonstrating how DERCHI enhances the overall performance of the electrical grid.
Future Trends and Challenges in the Development of DERCHI Systems
The development of DERCHI systems presents both exciting opportunities and significant challenges. These systems aim to enhance energy management by using decentralized resources. As we move forward, one key trend is the integration of artificial intelligence. AI can optimize energy distribution and consumption patterns. However, reliance on technology raises concerns about security and privacy.
Another challenge lies in regulatory frameworks. As DERCHI systems evolve, existing regulations may not keep pace. This misalignment can hinder innovation and deployment. Stakeholders must collaborate to adapt policies that support these systems. Additionally, public awareness is crucial. Many individuals remain uninformed about the benefits of DERCHI. Building trust takes time, and skepticism often arises.
Moreover, scalability poses an ongoing issue. Not all DERCHI implementations work seamlessly in every community. Variations in infrastructure can complicate uniform deployment. Enhancing interoperability between systems is essential for widespread adoption. There’s still much to learn and improve in this field. Reflection on past successes and failures will guide future advancements.
Article Source:
Developed and Managed by Infocom Network Private Limited.


